A Water-Cooled Condenser is a heat exchanger that uses water as the primary cooling medium to condense steam or other vapors back into liquid.
It is the most common and efficient type of condenser used in large-scale applications where water is readily available.
Simple Definition
A Water-Cooled Condenser is a device where steam is condensed by transferring its latent heat to a flow of cooling water. The key feature is that the water absorbs the heat from the steam, causing the steam to change phase into liquid water.
How It Works (The Core Principle)
The fundamental process is the same whether the condenser is a shell and tube, plate, or other type:
- Hot Steam Inlet: Exhaust steam from a turbine or engine enters the condenser.
- Cooling Water Circulation: Cold water is pumped from a source (like a river, sea, or cooling tower) and circulated through the condenser.
- Heat Transfer: The steam comes into contact with cold surfaces that are cooled by the water. The steam releases its latent heat of vaporization to the cooling water.
- Condensation: The steam condenses into liquid water (condensate).
- Separation: The condensate is collected for reuse, and the now-warm cooling water is discharged or cooled for reuse.
Types of Water-Cooled Condensers
There are several designs, but they fall into two main categories based on whether the cooling water and steam mix.
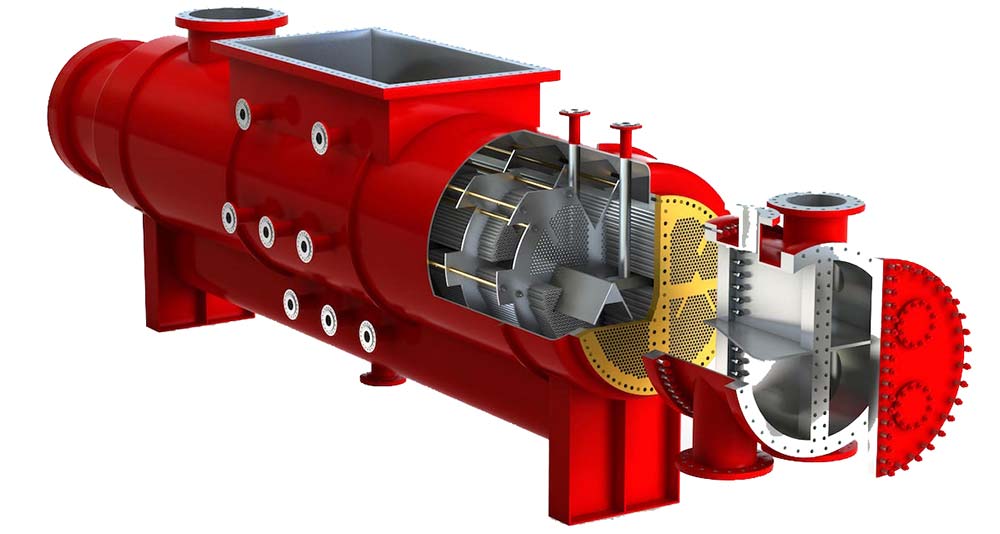
1. Surface Condensers (Indirect Contact)
This is the most important type for large power plants, as discussed in previous answers. The cooling water and steam do not mix.
- Shell and Tube Condenser: The most prevalent type.
- How it works: Cooling water flows inside the tubes. Exhaust steam surrounds the tubes in the shell and condenses on the outside of them.
- Advantage: Condensate is recovered in pure form for reuse in the boiler.
Advantages of Water-Cooled Condensers
- High Efficiency: Water is an excellent heat transfer medium, allowing for a very deep vacuum and high turbine efficiency.
- Consistent Performance: Less sensitive to ambient temperature fluctuations than air-cooled condensers (especially once-through systems).
- Compact Size: For the same heat duty, a water-cooled condenser is much smaller than an air-cooled one.
- Lower Power Consumption: The power required for water pumps is generally less than that needed for the massive fans of an air-cooled condenser.
- Condensate Recovery: In surface condensers, high-purity condensate is recovered, saving energy and water treatment costs.