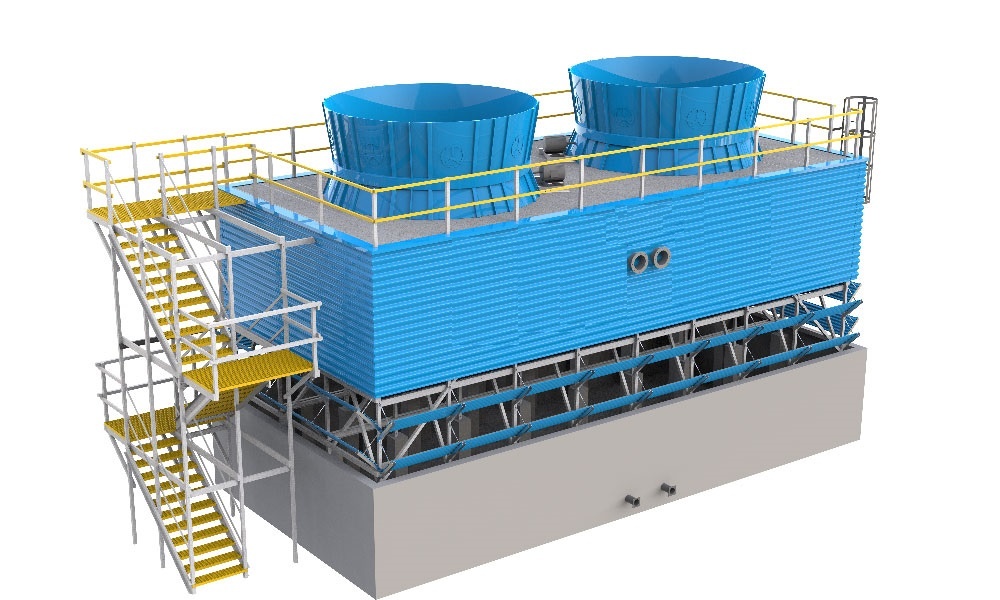
A Pultruded cooling tower refers to a cooling tower constructed using pultruded fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites instead of traditional materials like wood, metal, or conventional molded FRP. Pultrusion is a continuous manufacturing process that produces high-strength, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant profiles, making it an attractive option for cooling tower components.
Key Features of Pultruded Cooling Towers:
- Material Advantages:
- Corrosion Resistance: Unlike steel or wood, pultruded FRP does not rust, rot, or degrade from exposure to water and chemicals.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Stronger than wood and lighter than steel, reducing structural load.
- Dimensional Stability: Resists warping, swelling, or shrinking in humid/wet conditions.
- UV & Chemical Resistance: Can be formulated with additives to withstand harsh environments.
- Components Made via Pultrusion:
- Structural supports (beams, columns, frames)
- Cooling tower louvers
- Fill media supports
- Fan cylinders & casings
- Drift eliminators
- Benefits Over Traditional Cooling Towers:
- Longer Lifespan: No corrosion or biological degradation.
- Lower Maintenance: No need for painting, coating, or frequent replacements.
- Energy Efficiency: Lightweight materials reduce fan motor load.
- Customizable Designs: Pultruded profiles can be tailored for specific load requirements.
- Applications:
- Industrial cooling towers (power plants, refineries, HVAC systems)
- Evaporative coolers
- Water treatment plants
Comparison with Molded FRP Cooling Towers:
- Pultruded FRP offers better consistency in mechanical properties since it’s a continuous process.
- Molded FRP (hand-layup or filament winding) is better for complex shapes but may have variations in strength.
Challenges:
- Higher initial cost compared to wood or metal (though lifecycle costs are lower).
- Requires expertise in FRP structural design.