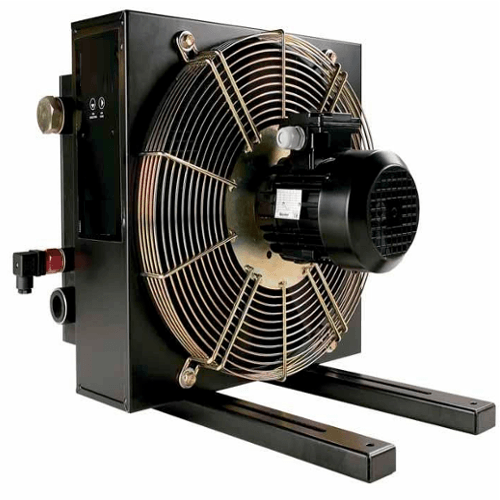
Air blast coolers are used for process cooling. Ambient air is forced over a heat exchanger to remove unwanted heat from a closed circuit containing process fluids or intermediate coolant.
An “air blast cooler” is a heat exchanger that uses forced air to cool a process fluid or intermediate coolant. Unlike air coolers that use evaporative cooling (like swamp coolers), air blast coolers don’t cool the air itself, but rather transfer heat away from a closed system. They are typically used in industrial settings where heat needs to be removed from a liquid or gas without direct contact with the cooling medium.
How Air Blast Coolers Work:
1. Process Fluid/Coolant:
A fluid containing heat (e.g., from a process or machine) flows through a heat exchanger (tubes or plates) within the air blast cooler.
2. Forced Air:
A fan blows ambient air over the heat exchanger, creating a flow of air that can transfer heat away from the fluid.
3. Heat Transfer:
The heat from the process fluid is transferred to the heat exchanger, and then the heat exchanger transfers the heat to the circulating air.
4. Cooling:
The now heated air is exhausted, while the process fluid or coolant leaves the cooler at a lower temperature, ready to return to the process or be used for its intended purpose.
Key Differences from Evaporative Air Coolers:
Cooling Medium:
Air blast coolers use air as a direct cooling medium, while evaporative coolers use the evaporation of water.
Humidity:
Air blast coolers don’t increase humidity as they don’t use water evaporation.
Application:
Air blast coolers are generally used for process cooling applications, like cooling fluids used in manufacturing, while evaporative coolers are used for room cooling in homes and offices