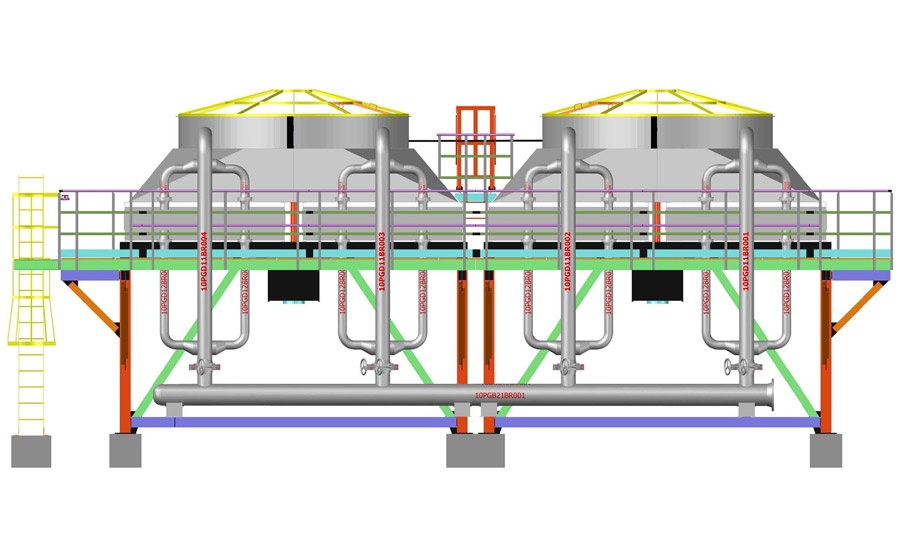
Air-Cooled Steam Condensers (ACSCs) in Power Plants & Industrial Systems
Air-cooled steam condensers (ACSCs) are specialized heat exchangers that convert exhaust steam from turbines back into water using ambient air cooling instead of water-cooled systems. They’re increasingly important in power generation and industrial processes where water conservation is critical.
1. Working Principle
- Steam Condensation: Low-pressure exhaust steam from turbines flows through finned tubes
- Air Cooling: Large fans force/pull ambient air across tube bundles
- Condensate Collection: Condensed water returns to the feedwater system
- Non-condensable Gas Removal: Vacuum system maintains proper pressure
2. Key Components
| Component | Function |
| Tube Bundles | Finned tubes for steam condensation |
| Axial Fans | Provide cooling airflow (forced/induced draft) |
| Steam Ducting | Distributes steam from turbine exhaust |
| Condensate Tank | Collects condensed water |
| Vacuum System | Maintains sub-atmospheric pressure |
| Air Removal System | Extracts non-condensable gases |
3.
System Configurations
A. Direct Dry Cooling (ACC)
·
Steam condenses directly in
air-cooled tubes
·
Used in most modern power
plants
·
No water consumption
B. Indirect Dry Cooling
(Heller System)
·
Steam condenses in surface
condenser
·
Cooling water loop rejects
heat to air-cooled heat exchangers
·
Lower efficiency but more
stable operation
C. Hybrid Wet/Dry Systems
·
Dry cooling with water spray
augmentation during peak loads
·
Balances water savings with
performance
4. Advantages vs. Water-Cooled Condensers
Zero water consumption – Critical for arid regions
Lower
environmental impact – No thermal pollution or water
discharge
Reduced
permitting – Avoids water rights issues
Flexible siting – Not limited to water sources
Lower
maintenance – No biofouling or scaling
5. Challenges & Limitations
Higher capital cost – Larger footprint and more equipment
Lower
efficiency – Performance varies with ambient temperature
Parasitic
power loss – Fan power reduces net output
Cold
weather issues – Potential freezing in winter
Air
Cooled Heat Exchanger Noise concerns – Large fan arrays
require mitigation
6. Design Considerations
·
Climate analysis – Design for peak summer temperatures
·
Tube layout – A-frame, horizontal, or vertical
configurations
·
Fan selection – Variable frequency drives for efficiency
·
Freeze protection – Tube bundle heating systems
·
Noise control – Low-noise fan designs and barriers
7. Applications
Power Generation
·
Thermal power plants (coal,
gas, biomass)
·
Solar thermal power plants
·
Geothermal plants
Industrial Processes
- Refineries
- Chemical plants
- District heating systems
8. Performance Optimization
- Variable speed fans – Adjust to load and ambient conditions
- Intelligent control systems – Optimize vacuum and fan operation
- Wind shields – Reduce performance degradation from crosswinds
- Advanced fin designs – Improve heat transfer efficiency
9. Maintenance Requirements
- Regular fin cleaning – Maintain airflow and heat transfer
- Fan maintenance – Bearing lubrication and alignment
- Leak detection – Steam and condensate systems
- Winterization – Freeze protection measures
Air-cooled steam condensers provide a water-smart solution for power plants and industrial facilities, particularly in water-scarce regions. While they involve higher initial costs and lower efficiency compared to water-cooled systems, their environmental benefits and operational advantages make them increasingly popular in sustainable energy systems.